ABOUT THE COURSE :
Learning Objectives :
- Introduce R as a programming language
- Introduce the mathematical foundations required for data science
- Introduce the first level data science algorithms
- Introduce a data analytics problem solving framework
- Introduce a practical capstone case study
Learning Outcomes:
- Describe a flow process for data science problems (Remembering)
- Classify data science problems into standard typology (Comprehension)
- Develop R codes for data science solutions (Application)
- Correlate results to the solution approach followed (Analysis)
- Assess the solution approach (Evaluation)
- Construct use cases to validate approach and identify modifications required (Creating)
INTENDED AUDIENCE: Any interested learner
PREREQUISITES: 10 hrs of pre-course material will be provided, learners need to practise this to be ready to take the course.
INDUSTRY SUPPORT: HONEYWELL, ABB, FORD, GYAN DATA PVT. LTD.
NPTEL Data Science for Engineers Week 1 Assignment Answer
Course layout
Week 1: Course philosophy and introduction to R
Week 2: Linear algebra for data science
1. Algebraic view – vectors, matrices, product of matrix & vector, rank, null space, solution of over-determined set of equations and pseudo-inverse)
2. Geometric view – vectors, distance, projections, eigenvalue decomposition
2. Geometric view – vectors, distance, projections, eigenvalue decomposition
Week 3: Statistics (descriptive statistics, notion of probability, distributions, mean, variance, covariance, covariance matrix, understanding univariate and multivariate normal distributions, introduction to hypothesis testing, confidence interval for estimates)
Week 4: Optimization
Week 5: 1. Optimization
2. Typology of data science problems and a solution framework
Week 6: 1. Simple linear regression and verifying assumptions used in linear regression
2. Multivariate linear regression, model assessment, assessing importance of different variables, subset selection
Week 7: Classification using logistic regression
Week 8: Classification using kNN and k-means clustering
NPTEL Data Science for Engineers Week 1 Assignment Answer
Week 1 : Assignment 1
Due date: 2025-02-05, 23:59 IST.
Assignment not submitted
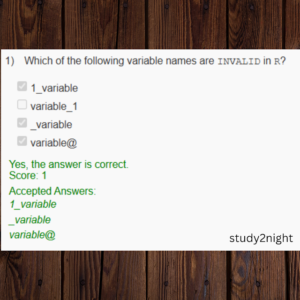
Q1. Which of the following variable names are INVALID in R?
a. 1_variable
b. variable_1
c. _variable
d. variable@
Answer: [ a ], [ c ], [ d ]
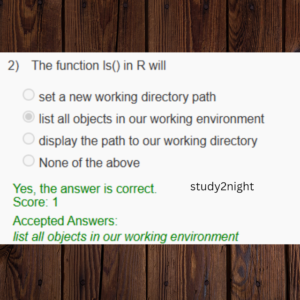
a. set a new working directory path
b. list all objects in our working environment
c. display the path to our working directory
d. None of the above
Answer: [ b ] list all objects in our working environment
Consider the following code snippet. Based on this, answer questions 3 and 4.
ID = c (1,2,3,4)
Patient_name = c ( “Ram”, “Shyam”, “Nandini”, “Maya” )
num.patient = 4
patient_list = list ( num.patient, ID, Patient_name )
Q3. Which of the following command is used to access the value “Shyam” ?
a. print(patient_list[3][2])
b. print(patient_list[[3]][1])
c. print(patient_list[[3]][2])
d. print(patient_list[[2]][2])
Answer: [ C ] print(patient_list[[3]][2])
Q4. What does the following R code produce?
x <- c (“apple”, “banana”, “cherry” )
x [2]
a. “apple”
b. “banana”
c. “cherry”
d. Error
Answer: [ B ] Banana
Q5. What is the output of following code?
x <- 10 + 5%%3
typeof (x)
a. double
b. integer
c. list
d. None of the above
Answer: [ a ] double
State whether the given statement is True or False.
Q6. The library reshape2 is based around two key functions named melt and cast.
a. True
b. False
Answer: [ a ] True
Q7. What does the following R code return?
x <- c ( 5,10,15,20 )
y <- x [ x > 10 ]
y
a. 5, 10, 15, 20
b. 15, 20
c. 10, 15, 20
d. Error
Answer: [ B ] 15, 20
Q8. What is the output of the following R code?
x <- 1
while ( x <= 3 ) {
print ( x )
x <- x+1
}
a. 1, 2, 3
b. 0, 1, 2
c. 1, 2, 3, 4
d. Error
Answer: [ a ] 1,2,3
Create the data frame using the code given below and answer questions 8 and 9.
student_data = data.frame(student_id=c(1:4),student_name=c(‘Ram’,‘Harish’,‘Pradeep’,‘Rajesh’))
Q9. Choose the correct command to add a column named student_dept to the dataframe student_data.
a. student_datastudent_dept=c(“Commerce”, “Biology”, “English”, “Tamil”)
b. student_data[“student_dept”]= c(“Commerce”,“Biology”, “English”,“Tamil”)
c. student_dept= student_data[c(“Commerce”,“Biology”,“English”,“Tamil”)]
d. None of the above
Answer: [ a ] [ b ]
student_datastudent_dept=c(“Commerce”, “Biology”, “English”, “Tamil”)
student_data[“student_dept”]= c(“Commerce”,“Biology”, “English”,“Tamil”)
Q10. Choose the correct command to access the element Tamil in the dataframe student_data.
a. student_data[[4]]
b. student_data[[4]][3]
c. student_data[[3]][4]
d. None of the above
Answer: [ C ] student_data[[3]][4]
Q11. The command to check if a value is of numeric data type is ______.
a. typeof()
b. is.numeric()
c. as.numeric()
d. None of the above
Answer: [ B ] is.numeric()
Q12. What will the following R code return?
mat <- matrix ( 1:9, nrow=3, ncol=3, byrow=TRUE )
mat [2,3]
a. 6
b. 5
c. 9
d. Error
Answer: [ a ] 6
Q13. What is the result of the following R code?
mat 1<- matrix ( 1:6, nrow=2, ncol=3)
mat 2<- matrix ( 7:12, nrow=2, ncol=3)
result <- mat1 + mat2
result {codeBox }
a. [1] 8 10 12
[2] 14 16 18
b. [1] 8 10 12 14 16 18
c. [1] 8 9 10 11 12 13
d. Error
Answer: